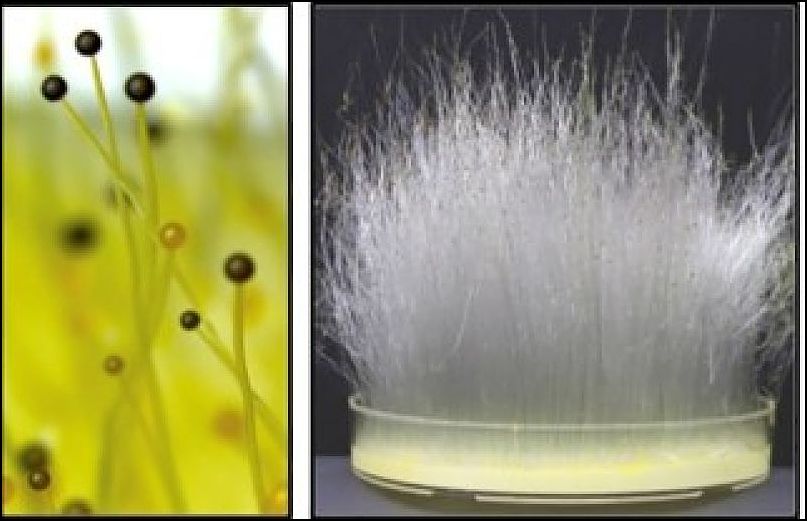
Phycomyces belongs to a basal fungal lineage, considered simpler and ancestral, yet the large (to a microbiologist) spore-bearing structures, called sporangiophores, respond to light, gravity, wind, and even the proximity of an object. Image: Corrochano et al. Current Biology (2016), with permission.